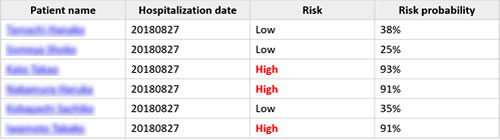
Infectious diseases have always been threatening lives throughout human history. Malaria, a distant memory in Japan, continues to infect more than 200 million people worldwide each year, mainly in Africa. According to World Health Organization (WHO), the estimated number of malaria fatalities was 405,000 in 2018, 94% of which occurred in Africa, and 67% was children under the age of five.
Malaria is transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito. When talking about pesticides used to prevent malaria, Japanese people may have a vivid memory of DDT (an organochlorine pesticide) used by the U.S. armed forces after the Second World War. In Japan, DDT played a key role in controlling lice and malarial mosquitoes in the post-war period when sanitary conditions were poor. However, the manufacture and use of DDT have been banned in many countries since environmental problems associated with its use were pointed out.
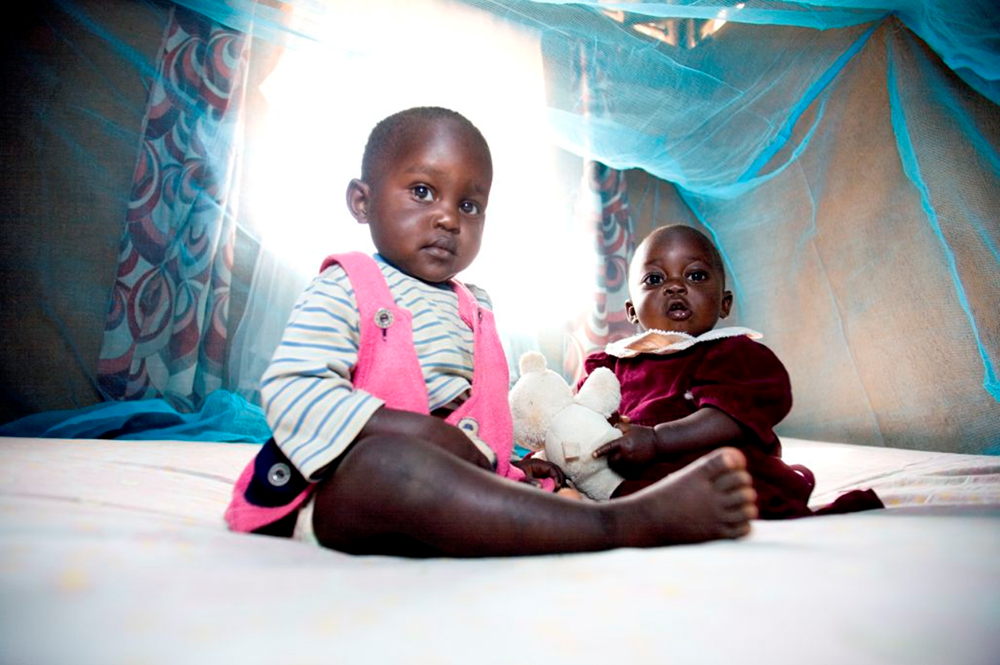
For half a century, Sumitomo Chemical has engaged, as a business, in mosquito vector control; measures to control or eliminate mosquitoes that transmit tropical infectious diseases. The company began its operation in 1913 as a producer of fertilizers, and has evolved pesticide technology as an extension of that business. A groundbreaking product developed in the second half of the 1990s using the technology cultivated over the years was Olyset® Net, a long-lasting insecticidal net impregnated with an insecticide effective against malaria-transmitting mosquitoes. The technology was originally applied in insect-repellent screen doors used in factories. In the 1990s the idea of applying this technology to malaria prevention was raised internally at Sumitomo Chemical, and this led to commercialization of a new product.
Prevention of the spread of malaria was already included in the United Nations Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) back in 2000, the predecessor of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Sumitomo Chemical has since distributed Olyset® Net through various international organizations. Olyset® Net was recommended in 2001 by the WHO as the world’s first long-lasting insecticidal net, and it has come into widespread use mainly in Africa where there are many malaria patients. The company also developed an indoor residual spray (IRS) as a malaria control product and made efforts to disseminate it. The spray exterminates Anopheles mosquitoes by exploiting their habit to rest on walls after biting humans.

Due in part to the contribution of such products, the worldwide malaria morbidity rate trended down toward 2010. However, it began showing an upward trend from around 2014, particularly in Africa. It has been reported that one of the causes for upward swing was an increased resistance of mosquitoes to the existing insecticide ingredients used in some regions. Sumitomo Chemical responded to this challenge by embarking on the development of SumiShield™ 50WG, an IRS that contains a new active ingredient. The company obtained WHO prequalification for the product in 2017 and began supplying it in Africa in 2018.
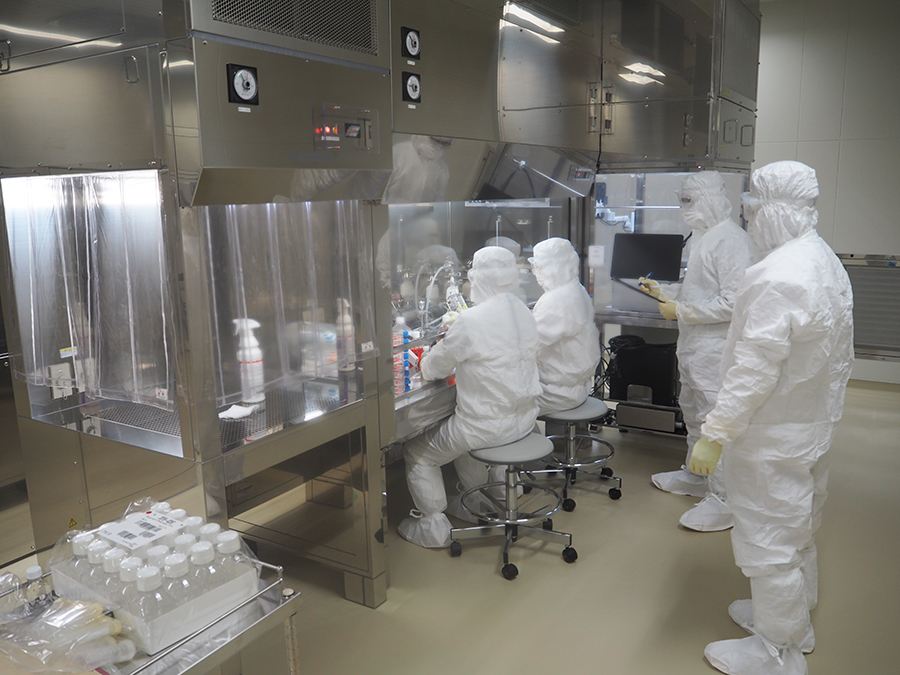
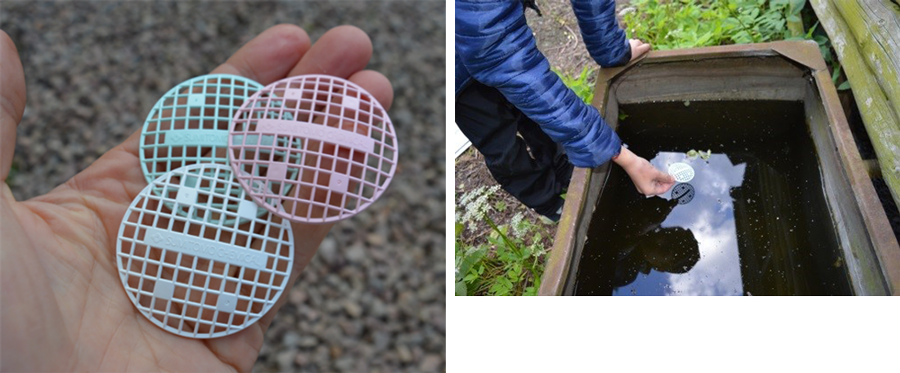
Since SumiShield™ 50WG must be sprayed in the right quantity evenly on walls, it is very important for us to demonstrate the correct use of the product to people in the field. Accordingly, Sumitomo Chemical employees travel to Africa, and disseminate the product bundled with technical guidance. The company has now moved into a phase to increase supply volume and accelerate dissemination. In addition to SumiShield™ 50WG, Sumitomo Chemical has launched several other products effective in preventing tropical infectious diseases. One example is SumiLarv® 2MR, a long-lasting larvicide for combating dengue fever and Zika fever, diseases similarly transmitted by mosquitoes. The company will continue its effort to contribute to the health of people in Africa and around the world through this business.

 EN
EN One-point explanation
One-point explanation