Social Issues addressed by Sumitomo —Compass for the Future—
Energy resource aggregation business launched.
Supply-demand adjustment for renewables based on “virtual power plant” technology
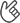 Decarbonization
Decarbonization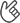 Local production for local consumption
Local production for local consumptionCarbon neutrality is a key concept in the drive to achieve sustainable economic growth in harmony with the Earth. The attainment of carbon neutrality goals is greatly dependent on measures taken in the energy sector, which accounts for the majority of greenhouse gas emissions.
In these circumstances, NEC is emphasizing carbon neutrality-related businesses in order to resolve social issues through its business. Specifically, NEC has been exploring the possibilities of the energy resource aggregation business, which seeks to realize more efficient and optimized energy management, development of decarbonization solutions, and commercialization in a circular economy. In October 2021, NEC entered the electricity supply-demand adjustment market as a resource aggregator (RA), with an eye to the eventual achievement of carbon neutrality in the energy sector. Amid the transition from fossil fuels to renewables, NEC intends to achieve carbon neutrality while also sharpening the company’s competitiveness.
NEC’s focus on the energy resource aggregation business is primarily prompted by recognition of the urgent need to decarbonize the energy sector. Increasing the ratio of renewable energy contributes to decarbonization, but it is difficult to balance supply and demand because the amount of renewable energy generated fluctuates greatly depending on weather conditions, which impedes the transition to renewables. NEC is proposing socially beneficial solutions through its energy resource aggregation business.
There are three principal issues. Firstly, a capability is needed to balance supply and demand. Secondly, it is necessary to decarbonize this capability by shifting from thermal power generation and other sources to renewable energy. Thirdly, demand must be optimized through demand response (DR) and other means in accordance with fluctuations on the supply side. While seeking solutions to these issues, it is essential to promote renewable energy so as to position it as the main power source, and sophisticated control of demand corresponding to fluctuations in power supply is essential. By utilizing its virtual power plant (VPP) technology, NEC realizes advanced supply-demand control, facilitating progress toward carbon neutrality as a resource aggregator managing and providing power facilities.
In order to equip the market with the capability to balance supply and demand, it is necessary to monitor the change in electricity demand in real time and respond to ever-changing conditions. This requires sophisticated control utilizing IT and forecasting technology, areas in which NEC excels. A VPP, which can serve as a balancer, is a virtual plant comprising various distributed power sources, such as solar power, wind power, in-house power generation facilities at business sites, and storage batteries for business use. IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and other technologies are deployed to achieve sophisticated control.
NEC is not only a leading source of cutting-edge IT but also offers cloud services for resource aggregators. By providing DR-enabled functions for VPPs and interfaces with other service providers, such as an aggregation coordinator (AC), as a service, NEC offers greater convenience to the many stakeholders involved in balancing supply and demand.
In addition to the business targeting the supply-demand balancing market, NEC is also supporting municipalities that are pursuing initiatives to achieve zero-carbon cities and local production for local consumption of energy. To meet the electricity demand of local companies within a particular area, such as a municipality, renewable energy generated in the area will be used to balance energy supply-demand through local production for local consumption of energy. Locally generated renewable energy and CO2-free electricity will be used, and any surplus electricity identified by monitoring the supply-demand relationship will be stored in storage batteries and discharged whenever there is a shortage of electricity supply in the grid. NEC’s technologies accumulated for VPP are well-suited for deployment in the supply-demand balancing market that the company believes is poised for growth going forward.
With its expanding energy resource aggregation business, NEC advocates a “cyclical ICT model” as a global concept that it aims to implement. In this model, NEC as the resource aggregator and resource partners, which have power generation facilities, play the key roles in circulating value in the energy sector. In pursuit of carbon neutrality, resource partners will invest to introduce renewable energy systems and storage batteries. NEC provides part of the energy generated by the equipment introduced by the resource partners to the supply-demand balancing market via the aggregation coordinator (AC) and gains revenue, which leads to revenue for resource partners. This cycle encourages new investment in decarbonization by resource partners.
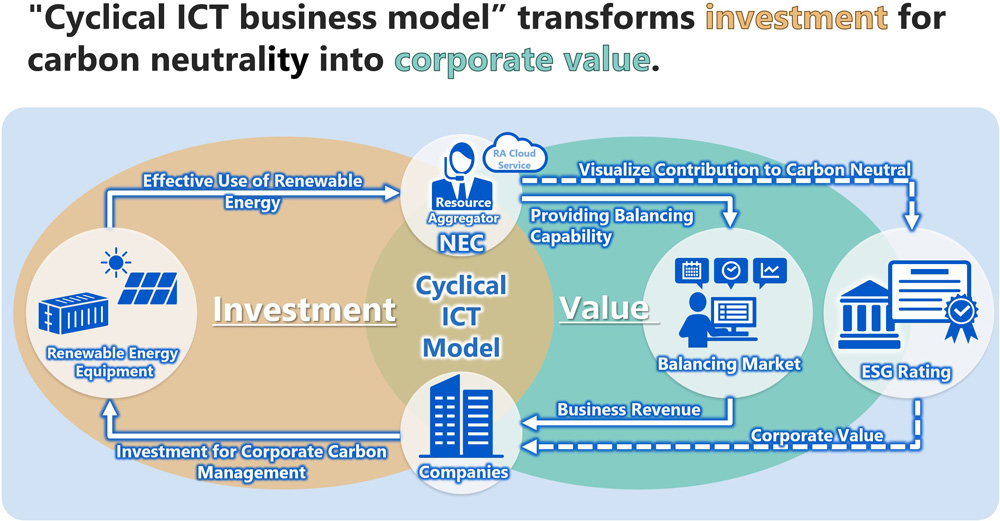
NEC will establish a cyclical ICT model to circulate value and achieve sustainable carbon neutrality, rather than engage in piecemeal investment in pursuit of carbon neutrality.


Read about initiatives to achieve a low-carbon society, aiming at net-zero greenhouse gas emissions since these emissions are implicated in global warming.

In view of ongoing globalization and the growing complexity of supply chains, companies need to respond appropriately to issues in supply chains.

The pace of workstyle reform is accelerating as the COVID-19 pandemic has prompted numerous companies to embrace novel ways of working.

For companies, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought the crucial importance of employee health into sharp focus.

Accelerating global warming poses serious business risks. Accordingly, companies need to formulate strategies and implement specific countermeasures from a medium- to long-term perspective.

Spurred by efforts to reduce environmental impacts and in line with increasing social needs, replacement of gasoline-powered vehicles with electric vehicles is accelerating.

Vigorous initiatives are afoot to tackle social issues by revitalizing communities and the interpersonal relationships that bind them together.

Poverty persists in contemporary Japan and the existence of child poverty is a grave concern.

In view of the continuing decline of Japan’s working age population, due to population aging coupled with a low birthrate, development of the next generation is an urgent issue.

The rapid progress in medicine in recent years is largely due to the efforts of not only universities and other research institutions but also of companies to develop cutting-edge technologies.

Numerous initiatives to promote industry and commerce at the regional and community level are underway, involving the use of renewable energy and thus contributing to decarbonization.

One-third of food produced is lost or wasted globally, amounting to about 1.3 billion tons per year. Food loss and waste is a pressing issue in need of a solution.

Companies are addressing a wide range of issues so that people and companies can coexist in harmony with the global environment.
In addition to natural disasters, there are various types of hazards whose nature, incidence and severity are changing with the times. Resilience and flexibility are indispensable in dealing with them.

Read about initiatives to achieve sustainable regional revitalization. The attributes and resources that each region can offer are leveraged to strengthen local economies and overcome the problem of population decline.